T226 White Paper
July 2003 (Rev C)
10
The MMS server, through which MMS messages are
sent, supports flexible addressing (to both normal
phone numbers (MSISDN) and email accounts),
which makes the user interface more friendly and
allows greater control for operators. The MMS server,
moreover, is responsible for the instant delivery of
MMS.
MMS technical features
The MMS standard, just like SMS, offers store-and-
forward transmission (instant delivery) of messages,
rather than a mailbox-type model. MMS is a person-
to-person communications solution, meaning that the
user gets the message directly into the mobile. Unlike
SMS, the MMS standard uses WAP as its bearer
protocol. MMS will take advantage of the high speed
data transport technologies such as GPRS and support
a variety of image, video and audio formats to
facilitate a complete communication experience.
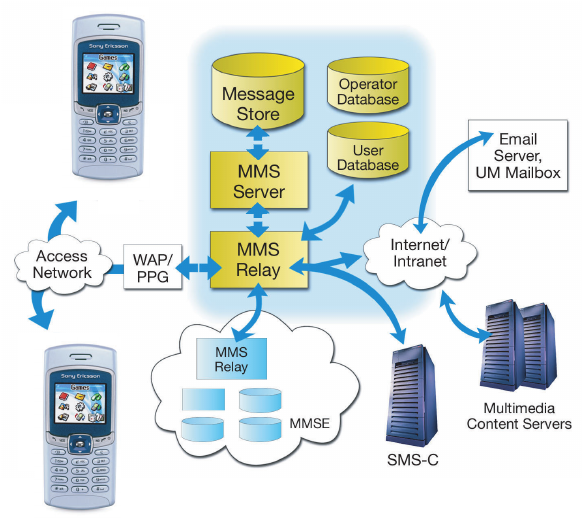
Architecture
The MMS Center (MMS-C) is comprised of the MMS
Server, the MMS Proxy-Relay and the MMS Store.
The MMS Center is the central element of the MMS
network architecture, providing storage and
operational support, enabling instant delivery of
multimedia messages from terminal-to-terminal and
terminal-to-email, and supporting flexible addressing.
The center’s MMS Proxy-Relay interacts with the
application being run on the MMS-enabled terminal to
provide various messaging services. WAP is used as
bearer of an MMS message between the MMS-C and
the MMS client (application). The WAP Gateway is
used for delivery and retrieval of messages.
Message conversion
The MMS-C is able to perform limited message
conversion - for example, from MMS to SMS - so that
processing and air time is not wasted in sending
messages to mobile terminals that do not have
adequate capability to receive them. It also handles
service aspects such as store and forward, guaranteed
delivery, subscriber preferences, operator constraints,
and billing information. The MMS-C also vouches for
high quality messaging, e.g. by format conversion.
This means that the MMS-C recognizes which formats
are supported in the mobile phone, and adapts the
MMS messages to these formats.
OTA configuration
Users can easily get MMS into their phone. MMS
supports OTA, meaning that the user does not have to
configure the settings manually.
The configuration is done by the operator.
Figure 3. The architecture of MMS


















