T226 White Paper
July 2003 (Rev C)
19
Using GPRS in the T226
Instead of occupying an entire voice channel for the
duration of a data session, the T226 sends/receives data
in small packets, as needed, much like IP on the
Internet. Because of this, the T226 maintains a constant
online connection. Its data transmission abilities are
summoned by the application in use on an as-needed
basis.
The GPRS specification includes four coding schemes
– CS1, CS2, CS3 and CS4 – that allow data speeds of
9,050 bps, 13,400 bps, 15,600 bps and 21,400 bps
respectively using one time slot. The T226 works with
all four coding schemes, but data speed will naturally
vary according to network configuration. At the
moment, CS3 and CS4 are not supported in any live
network, i.e., present speed is limited to 40,200 bps
using three time slots.
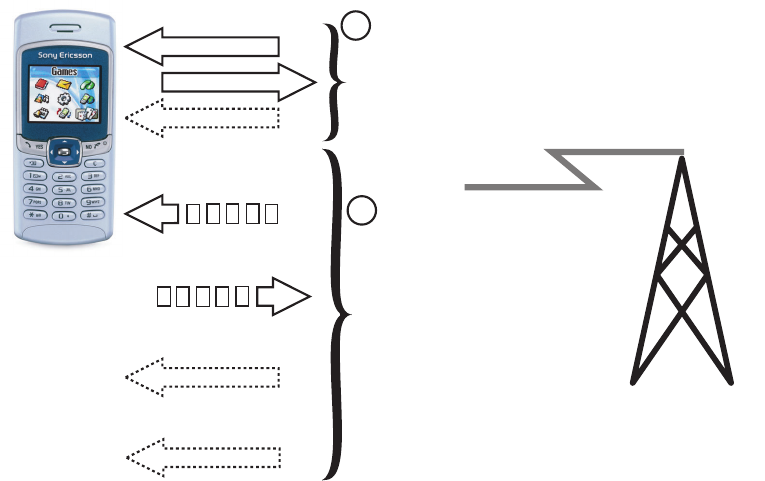
The GSM system limits the ability to use all eight time
slots, so the T226 uses up to three time slots for
receiving data, and one slot for transmitting (3+1). This
means that for CS4, the speed for receiving data is up
to 64,200 bps and up to 21,400 bps for sending data.
Information about the identity of the phone and the
characteristics of the connection are described in the
PDP (Packet Data Protocol) context. This information
is stored both in the phone and in the mobile network,
so that each phone is identified and “visible” to the
system.
Using GPRS with the T226 has several
advantages, for example:
• All connection settings can be managed by
using the data connections feature.
• High speed
Gain access automatically to increased band-
width when downloading images, etc.
• Cost efficient
Use transmission capacity only when needed,
GSM
9,600/14,400
9,600/14,400
9,050/13,400/
15,600/21,400
1
14,400, 19,200 or 28,800 bps (HSCSD
)
GPRS
9,050, 13,400,
15,600, 18,100,
21,400, 26,800,
27,150, 31,200
40,200, 42,800,
46,800 or 64,200 bps
2
9,600/14,400
9,600 bps
9,050/13,400/
15,600/21,400
9,050/13,400/
15,600/21,400
9,050/13,400/
15,600/21,400
Figure 4 A comparison between GSM and GPRS
1. A normal GSM call uses only one of eight repeat-
ing time slots in the GSM channel, giving a data speed
of 9,600 bps. The T226 supports a more efficient cod-
ing scheme, giving data speeds of up to 14,400 bps
(with necessary network support). Furthermore, High
Speed Circuit Switched Data (HSCSD) adds the possi-
bility of using two time slots for receiving data,
increasing the data speed to as much as 28,800 bps
(network dependent).
2. In GPRS, data is sent in packets, with up to three
time slots being combined to provide the necessary
bandwidth. The T226 is prepared to support 3+1 time
slots (three slots for receiving data and one slot for
transmitting data), giving speeds of up to 64,200 bps
for receiving data, depending on coding scheme.


















