Rockwell Automation Publication 1412-UM001D-EN-P - September 2012 89
Mathematical Formulas For Various Parameters Appendix C
Ratios
Various Types of Energy
Total active energy consumed:
Wh[0][3] = Wh[0][0] + Wh[0][1] + Wh[0][2]
Total apparent energy consumed:
VAh[0][3] = VAh[0][0] + VAh[0][1] + VAh[0][2]
Total reactive capacitive energy consumed:
VARhC[0][3] = VARhC[0][0] + VARhC[0][1] + VARhC[0][2]
Total reactive inductive energy consumed:
VARhL[0][3] = VARhL[0][0] + VARhL[0][1] + VARhL[0][2]
PF[i] = i + 1 phase power factor
W[i]
VA[i]
DPF[i] = cos(φ[i])
i + 1 phase displacement factor
Tan[i] = tan(φ[i])
i + 1 phase tangent
PF[3] =
PF[0] + PF[1] + PF[2]
3
Total power factor
DPF[3] =
DPF[0] + DPF[1] + DPF[2]
3
Total shift factor
Tan[3] =
Tan[0] + Tan[1] + Tan[2]
3
Total tangent
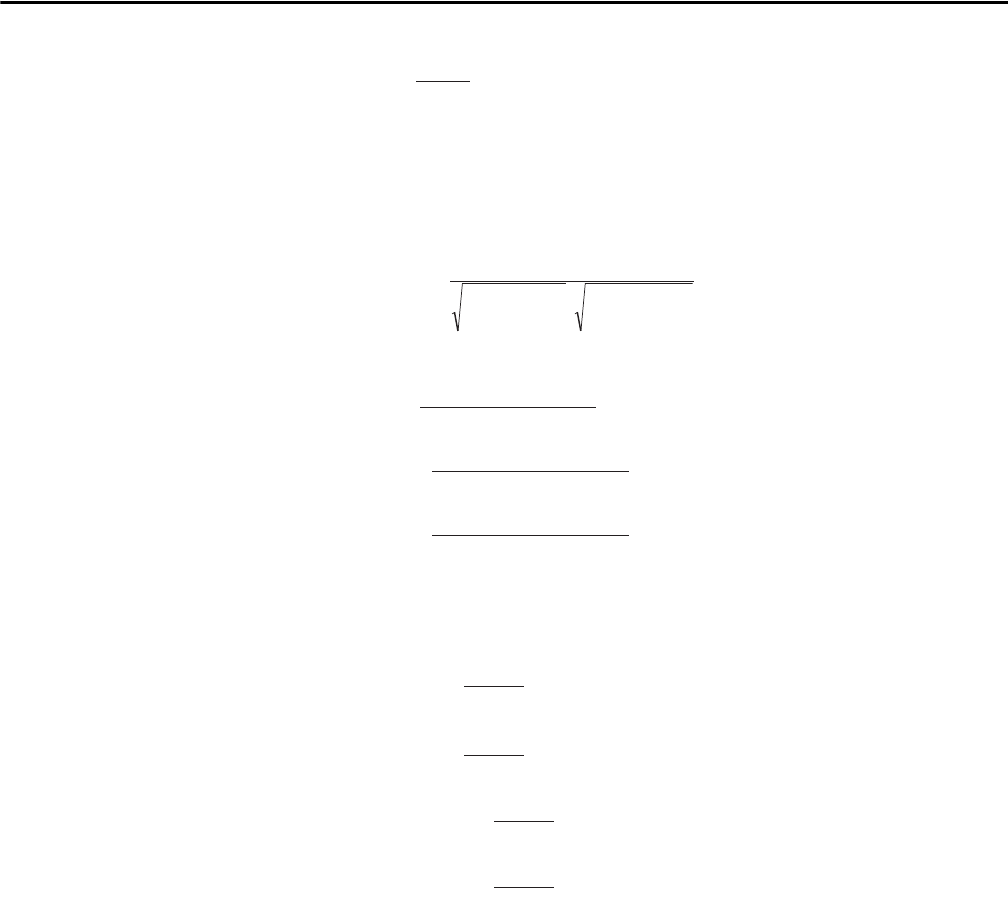
cos(φ[i]) =
[][ ]
Cosine angle between voltage
fundamental and i + 1 phase curren
NSS-1
0
2
niVF
[][ ]
niAF
n
∑
=
[][ ]
NSS-1
0
niVF
n
∑
=
2
[][ ]
NSS-1
0
niAF
n
∑
=
.
Wh
[
0
][
i
]
=
Active energy consumed phase i + 1
W[i]
3600
∑
Tint
VAh
[
0
][
i
]
=
Apparent energy consumed phase i + 1
VA[i]
3600
∑
Tint
VARhL
[
0
][
i
]
=
for VAR[i] ≥0
Reactive inductive energy consumed phase i + 1
VAR[i]
3600
∑
Tint
VARhC
[
0
][
i
]
=
for VAR[i] ≤0
Reactive capacitive energy consumed phase i + 1
3600
∑
Tint
–VAR[i]
