3.22
ENGINE
4. Measure free length of spring with a Vernier caliper. Check
spring for squareness. Compare to specifications. Replace
spring if either measurement is out of specification
5. Remove valve seals. CAUTION: Replace seals whenever
the cylinder head is disassembled. Hardened, cracked or
worn valve seals will cause excessive oil consumption and
carbon buildup.
Valve Inspection
1. Remove all carbon from valve with a soft wire wheel.
2. Check valve face for runout, pitting, and burnt spots. To
check for bent valve stems, mount valve in a drill or use “V”
blocks and use a dial indicator.
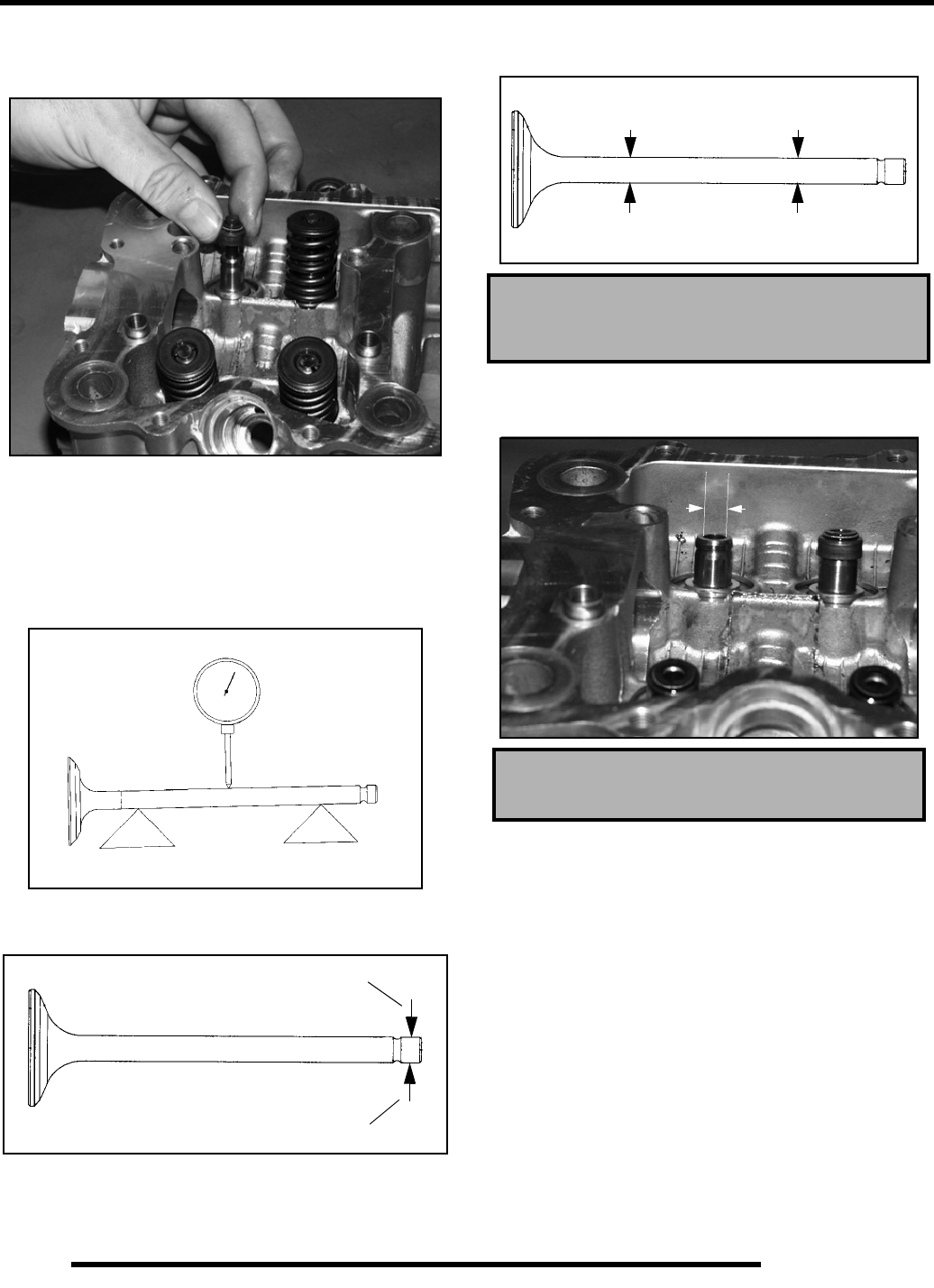
3. Check end of valve stem for flaring, pitting, wear or damage
(A).
4. Inspect split keeper groove for wear or flaring of the keeper
seat area (B). NOTE: The valves cannot be re-faced or end
ground. Valves must be replaced if worn, bent, or damaged.
5. Measure diameter of valve stem with a micrometer in three
places and in two different directions (six measurements
total). Compare to specifications.
6. Measure valve guide inside diameter at the top middle and
end of the guide using a small hole gauge and a micrometer.
Measure in two directions, front to back and side to side.
7. Subtract valve stem measurement to obtain stem to guide
clearance.
NOTE: Be sure to measure each guide and valve
combination individually
8. Replace valve and/or guide if clearance is
excessive.Compare to specifications.
NOTE: If valve guides are replaced, valve seats must be
reconditioned. Refer to Valve Seat Reconditioning for
procedure.
A
B
Valve Stem Diameter:
Intake: .2343-.2348” (5.950-5.965 mm)
Exhaust: .2341-.2346” (5.945-5.960 mm)
Valve Guide I.D.:
.2362-.2367” (6.0-6.012 mm)
Measure valve stem in several places
