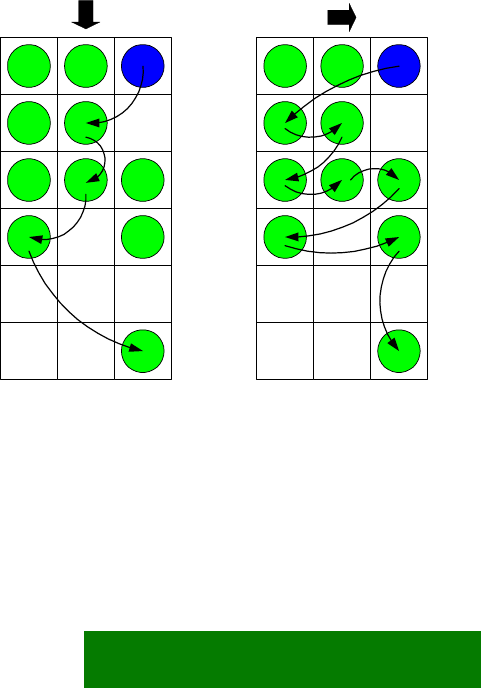
The browsing in grids that scroll vertically resembles traditional scrolling in text
editors, based on the idea that the user can always move to the correct row first and
then move within the row to the correct item. The following rules are applied:
Empty cells are skipped: the focus is never on an empty cell. ·
·
·
·
·
·
An exception to this occurs when the user is moving items around in a grid; in
that situation all cells are accessible.
When browsing down or up, the focus is moved to the adjacent cell directly
below or above the current cell, if that cell is filled. In case it is empty, the
nearest cell on the same row gets the focus. If all cells on the row are empty, the
search continues on the next row in the same direction, and so on until a filled
cell is found.
When browsing right, the focus moves to the following filled cell on the same
row. If there are no filled cells in that direction on the row, the search continues
from the beginning of the next row, and so on until a filled cell is found.
Browsing left moves the focus to the previous filled cell on the same row, or
continues searching from the end of the previous row. Using only the right or left
scroll key, the user can thus go through every item in the grid, regardless of the
distribution of items in it.
The grid is scrolled (moved within the view) only when the item that is becoming
focused is not fully visible already.
By default, grids do not loop vertically from the end to the beginning or vice
versa.
a. b.
Figure 5-5. Examples of moving the focus in a grid, starting from top right:
a. Only Scroll down commands used.
b. Only Scroll right commands used.
29


















