Chapter 4 Timer Functions
64
8-bit Timer Operation (timers 2, 3)
If TM2IO input is selected as the
clock source and the value of
binary counter 2 is to be read
during operation, select
synchronized TM2IO input to avoid
reading data that may be
incomplete during count-up
transitions. However, with
synchronized TM2IO input, it is not
possible to return from
STOP/HALT modes.
■ Event Count Function (timers 2, 3)
Settings for the event count function are listed below. Timer 2 is used as an example.
(1) Set the TM2EN flag of the timer 2 mode register (TM2MD) to "0" to stop the count
operation of timer 2.
(2) Use the TM2CK2 to 0 flags of the TM2MD register to select TM2IO input or
synchronous TM2IO input as the clock source.
(3) Set the TM2PWM flag of the TM2MD register to "0" so that normal timer operation is
selected.
(4) Set a value in compare register 2 (TM2OC).
(5) Set the TM2EN flag of the TM2MD register to "1" to start the timer.
(6) When timer 2 begins operation, binary counter 2 will count upward from X'00'.
(7) When the value of binary counter 2 matches that of the TM2OC register, the timer 2
interrupt request flag is set, and the binary counter 2 is reset to X'00' and begins to count
upward again.
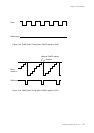
When synchronized TM2IO is selected, the timer 2 clock source is synchronized with the system
clock after a transition of the TM2IO input signal. Binary counter 2 counts upward based on a
signal synchronized to the system clock. Therefore, correct values can be read from binary counter
2.
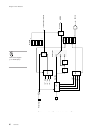
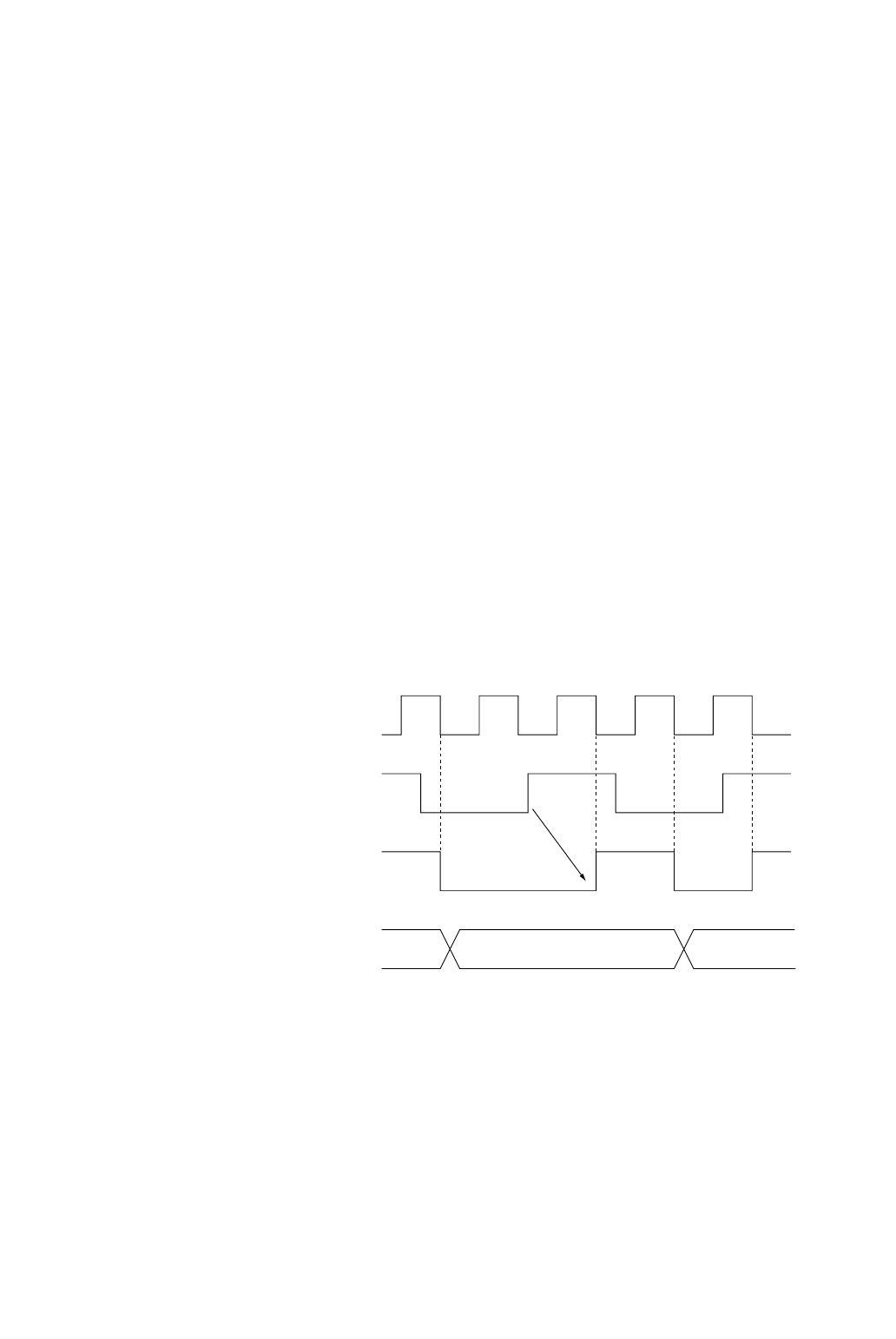
Figure 4-2-2 Timer 2 Event Counter Timing
(when synchronous TM2IO input is selected)
CPU system clock
(fs)
TM4IO input
Synchronous
circuit output
Binary counter n n+1