832 | Private VLANs
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
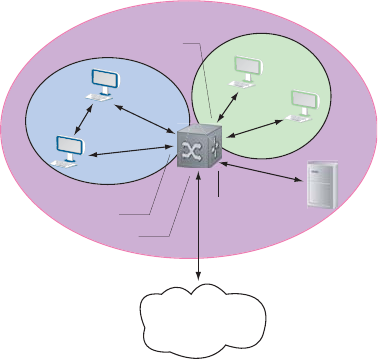
There are three types of ports in PVLAN:
• Host Ports—these ports are the ones that Private VLAN aims to isolate. They are connected to
end-stations.
• Promiscuous Ports—these ports are members of the primary VLAN, and function as gateways to the
primary and secondary VLANs.
• Trunk Ports—trunk ports carry tagged traffic between switches. They have promiscuous and trunk
ports as members.
Figure 39-2. PVLAN: Primary and Secondary VLANs
Important Points to Remember
• Even if secondary VLANs are operationally down, if the primary VLAN is operationally up, Layer 3
traffic is still be transmitted across the secondary VLANs.
• PVLAN ports cannot be added to regular VLANs. Conversely, regular VLAN ports cannot be added to
PVLANs.
• If a promiscuous or host port is untagged in a VLAN, and it receives a tagged packet in the same
VLAN, the packet will NOT be dropped.
• A primary VLAN and each of its secondary VLANs decrement the available number of VLAN IDs in
the switch.
Configure Private VLANs
Configuring Private VLANs is a 3-step process:
1. Configure PVLAN Ports
2. Place PVLAN Ports in a Secondary VLAN
3. Place the Secondary VLANs in a Primary VLAN
Network
Server
Promiscuous
Port
Trunk Port
Host Port
Host Port
Primary VLAN
Community
VLAN
Isolated
VLAN
