Positioning
70
Positioning
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a worldwide radio
navigation system that includes 24 satellites and their
ground stations that monitor the operation of the
satellites. Your device has an internal GPS receiver.
A GPS terminal, such as the GPS receiver in your device,
receives low-power radio signals from the satellites, and
measures the travel time of the signals. From the travel
time, the GPS receiver can calculate its location to the
accuracy of meters.
The coordinates in the GPS are expressed in degrees and
decimal degrees format using the international WGS-84
coordinate system.
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is operated by the
government of the United States, which is solely
responsible for its accuracy and maintenance. The
accuracy of location data can be affected by adjustments
to GPS satellites made by the United States government
and is subject to change with the United States
Department of Defense civil GPS policy and the Federal
Radionavigation Plan. Accuracy can also be affected by
poor satellite geometry. Availability and quality of GPS
signals may be affected by your location, buildings,
natural obstacles, and weather conditions. The GPS
receiver should only be used outdoors to allow reception of
GPS signals.
GPS should only be used as a navigation aid. It should not
be used for precise location measurement and you should
never rely solely on location data from the GPS receiver for
positioning or navigation.
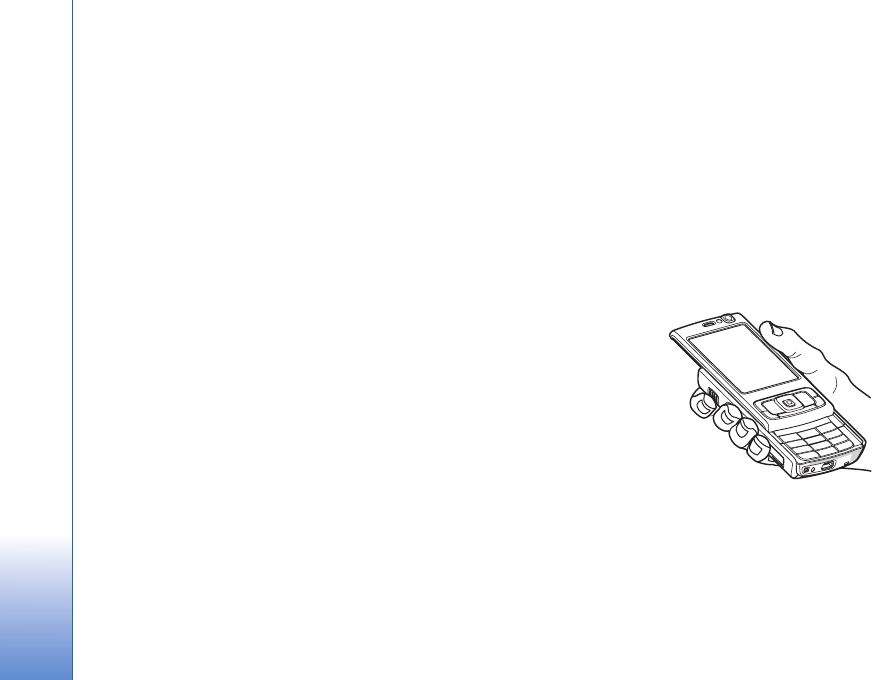
GPS receiver
The GPS receiver is
located in the bottom of
the device. When using
the receiver, slide the
numeric keypad open
and hold the device
upright in your hand at
an angle of about 45
degrees, with a clear
view of the sky.
Establishing a GPS connection may take from a couple of
seconds to several minutes. Establishing a GPS connection
in the car may take longer.
The GPS receiver takes its power from the battery. Using
the GPS receiver may drain the battery faster.


















