80 Working With Company E-mails
8.5 E-mail Security
Windows Mobile on your device protects your Outlook e-mails through Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail
Extension (S/MIME), which allows you to digitally sign and encrypt your messages.
Digitally signing a message applies your certificate with the authorization key to the message. This proves to
the recipient that the message is from you and not from an impostor or a hacker, and that the message has
not been altered.
Encryption protects the privacy of your message by converting it from plain, readable text into cipher
(scrambled) text. Only the recipient who has the authorization key can decipher the message.
Requirement S/MIME encryption and digital signatures for Windows Mobile-based devices are available only with
Exchange Server 2003 SP2 or a later version that supports S/MIME. If your company is not using
one of these products, or you have not completed your first synchronization with the Exchange
Server, these options are unavailable.
Note You can encrypt a message with or without a certificate. However, to read an encrypted message, you need a valid
certificate to decrypt it.
To individually sign and encrypt a new message
1. Tap Start > Messaging > Outlook E-mail.
2. Tap Menu > New to create a new message.
3. Tap Menu > Message Options.
4. From the Security list, select whether to encrypt only, sign the message only, or do both.
5. Tap OK.
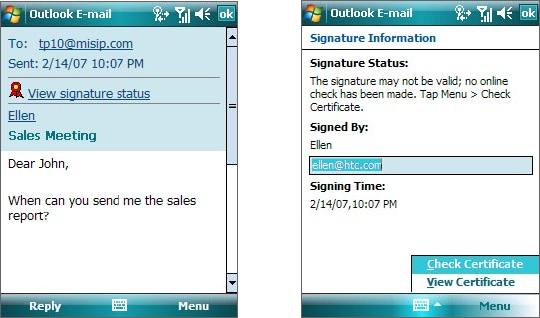
To verify the digital signature on a signed message you receive
1. Open the Outlook e-mail message that has been digitally signed.
2. At the top of the message, tap View Signature Status.
3. Tap Menu > Check Certificate.
To view the details of the certificate in the message, tap Menu > View Certificate.
Note There can be several reasons why a digital signature is not valid. For example, the sender’s certificate may
have expired, it may have been revoked by the certificate authority, or the server that verifies the certificate is
unavailable. Contact the sender to report the problem.


















