22 Getting started
Benefits include:
• Additional data protection. An independent copy of a volume (versus logical copy through snapshot)
provides additional data protection against a complete master volume failure. If the source master
volume fails, the volume copy can be used to restore the volume to the point in time the volume copy
was taken.
• Non-disruptive use of production data. With an independent copy of the volume, resource contention
and the potential performance impact on production volumes is mitigated. Data blocks between the
source and the copied volumes are independent (versus shared with snapshot) so that I/O is to each
set of blocks respectively; application I/O transactions are not competing with each other when
accessing the same data blocks.
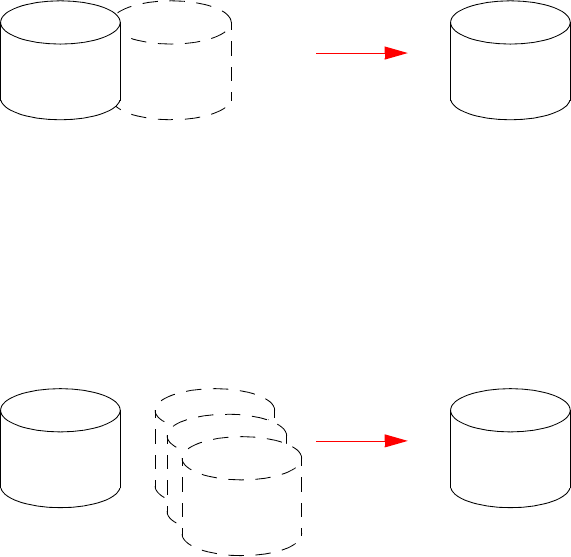
The following figure illustrates how volume copies are created.
Figure 3 Creating a volume copy from a master volume or a snapshot
Guidelines to keep in mind when performing a volume copy include:
• The destination vdisk must be owned by the same controller as the source volume.
• The destination vdisk must have free space that is at least as large as the mount of space allocated to
the original volume. A new volume will be created using this free space for the volume copy.
• The destination vdisk does not need to have the same attributes (such as disk type, RAID level) as the
volume being copied.
• Once the copy is complete, the new volume will no longer have any ties to the original.
• Volume Copy makes a copy from a snapshot of the source volume; therefore, the snap pool for the
source volume must have sufficient space to store snapshot data when performing this copy.
Source volume Transient snapshot Data transfer New volume
1. Volume copy request is made with a standard volume or a master volume as the source.
3. A new volume is created for the volume copy, and a hidden, transient snapshot is created.
4. Data is transferred from the transient snapshot to the new volume.
5. On completion, the transient volume is deleted and the new volume is a completely independent copy of
the master volume, representing the data that was present when the volume copy was started.
Creating a volume copy from a standard or master volume
Master volume
Snapshot(s) Data transfer New volume
1. A master volume exists with one or more snapshots associated with it. Snapshots can be in their original
Creating a volume copy from a snapshot
state or they can be modified.
2. You can select any snapshot to copy, and you can specify that the modified or unmodified data be copied.
3. On completion, the new volume is a completely independent copy of the snapshot. The snapshot remains,
though you can choose to delete it.
2. If the source a standard volume, it is converted to a master volume and a snap pool is created.


















