HP StorageWorks 2000 G2 Modular Smart Array Reference Guide 85
External details for connUnitPortTable
Configuring SNMP event notification in SMU
1. Verify that the storage system’s SNMP service is enabled; see Changing management interface settings
on page 33.
2. Configure and enable SNMP traps; see Configuring SNMP notification on page 34.
SNMP management
You can manage storage devices using SNMP with a network management system such as HP System
Insight Manager (SIM), or HP Instant Support Enterprise Edition (ISEE). See their documentation for
information about loading MIBs, configuring events, and viewing and setting group objects.
In order to view and set system group objects, SNMP must be enabled in the storage system; see Step 4:
Enabling system-management services on page 29.
Enterprise trap MIB
The following pages show the source for the HP enterprise traps MIB, msa2000traps.mib. This MIB
defines the content of the SNMP traps that 2000 G2 Modular Smart Array storage systems generate.
-- ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
-- MSA2000 Array MIB for SNMP Traps
--
-- $Revision: 11692 $
--
-- Copyright (c) 2008 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
-- Copyright (c) 2005-2008 Dot Hill Systems Corp.
-- Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession,
-- use or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and 12.212, Commercial Computer
-- Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial
-- Items are licensed to the U.S. Government under vendor's standard commercial
-- license.
--
-- MSA2000traps MIB Revision
-- ==========================
-- Revision 1.1 2008/02/27
-- Initial revision
-- Revision 1.2 2008/03/18
-- Updated copyright notice
--
-- ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
MSA2000TRAPS-MIB
-- Last edit date: Feb 27th, 2008
DEFINITIONS ::= BEGIN
IMPORTS
enterprises
FROM RFC1155-SMI
TRAP-TYPE
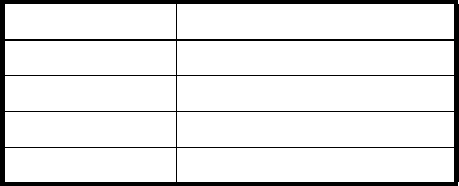
Table 13 connUnitPortTable index and name values
connUnitPortIndex connUnitPortName
1 Host Port 1 (Controller A)
2 Host Port 2 (Controller B)
3 Host Port 1 (Controller A)
4 Host Port 2 (Controller B)


















