24 Getting started
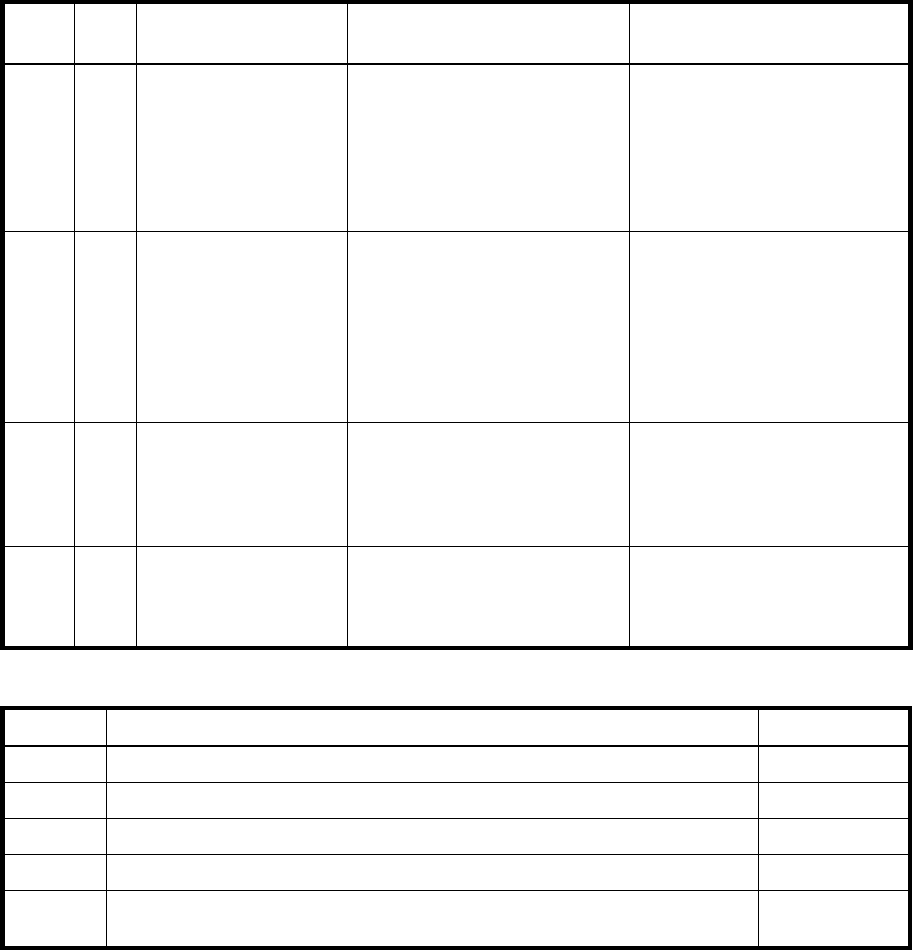
5 3 Block-level data striping
with distributed parity
Best cost/performance for
transaction-oriented networks;
very high performance and data
protection; supports multiple
simultaneous reads and writes;
can also be optimized for large,
sequential requests
Write performance is slower than
RAID 0 or RAID 1
6 4 Block-level data striping
with double distributed
parity
Best suited for large sequential
workloads; non-sequential read
and sequential read/write
performance is comparable to
RAID 5
Higher redundancy cost than
RAID 5 because the parity
overhead is twice that of RAID 5;
not well-suited for
transaction-oriented network
applications; non-sequential write
performance is slower than RAID
5
10
(1+0)
4 Stripes data across
multiple RAID-1
sub-vdisks
Highest performance and data
protection (can tolerate multiple
disk failures)
High redundancy cost overhead:
because all data is duplicated,
twice the storage capacity is
required; requires minimum of four
disks
50
(5+0)
6 Stripes data across
multiple RAID-5
sub-vdisks
Better random read and write
performance and data protection
than RAID 5; supports more disks
than RAID 5
Lower storage capacity than RAID
5
Table 6 Vdisk expansion by RAID level
RAID level Expansion capability Maximum disks
NRAID Cannot expand. 1
0, 3, 5, 6 You can add 1–4 disks at a time. 16
1Cannot expand. 2
10 You can add 2 or 4 disks at a time. 16
50 You can add one sub-vdisk at a time. The added sub-vdisk must contain the same
number of disks as each of the existing sub-vdisks.
32
Table 5 RAID level comparison (continued)
RAID
level
Min.
disks
Description Strengths Weaknesses


















