HP StorageWorks 2000 G2 Modular Smart Array Reference Guide 25
About size representations
In SMU panels, parameters such as names of users and volumes have a maximum length in bytes. ASCII
characters are 1 byte; most Latin (Western European) characters with diacritics are 2 bytes; most Asian
characters are 3 bytes.
Operating systems usually show volume size in base 2. Disk drives usually show size in base 10. Memory
size is always shown in base 2. In SMU, the base for entry and display of storage-space sizes can be set
per user or per session. When entering storage-spaces sizes only, either base-2 or base-10 units can be
specified.
The locale setting determines the character used for the decimal (radix) point, as shown below.
About the system date and time
You can change the storage system's date and time, which are displayed in the System Status panel. It is
important to set the date and time so that entries in system logs and event-notification email messages have
correct time stamps.
You can set the date and time manually or configure the system to use Network Time Protocol (NTP) to
obtain them from a network-attached server. When NTP is enabled, and if an NTP server is available, the
system time and date can be obtained from the NTP server. This allows multiple storage devices, hosts, log
files, and so forth to be synchronized. If NTP is enabled but no NTP server is present, the date and time are
maintained as if NTP was not enabled.
NTP server time is provided in Universal Time (UT), which provides several options:
• If you want to synchronize the times and logs between storage devices installed in multiple time zones,
set all the storage devices to use UT.
• If you want to use the local time for a storage device, set its time zone offset.
• If a time server can provide local time rather than UT, configure the storage devices to use that time
server, with no further time adjustment.
Whether NTP is enabled or disabled, the storage system does not automatically make time adjustments,
such as for U.S. daylight savings time. You must make such adjustments manually.
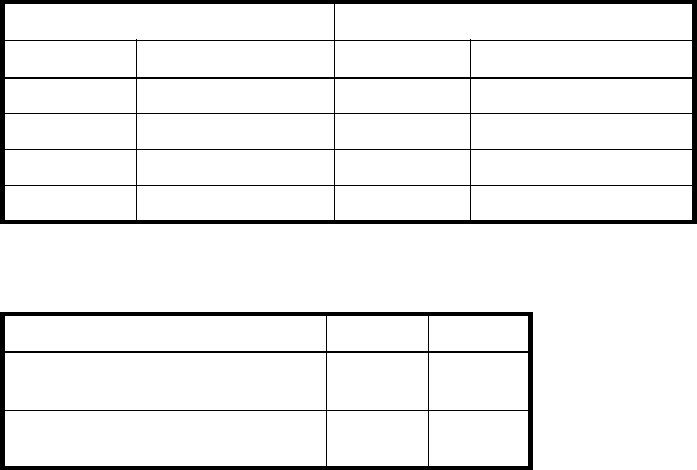
Table 7 Size representations in base 2 and base 10
Base 2 Base 10
Unit Size in bytes Unit Size in bytes
KiB (kibibyte) 2
10
(1,024) KB (ki lo byte) 10
3
(1,000)
MiB (mebibyte) 2
20
(1,048,576) MB (megabyte) 10
6
(1,000,000)
GiB (gibibyte) 2
30
(1,073,741,824) GB (gigabyte) 10
9
(1,000,000,000)
TiB (tebibyte) 2
40
(1,099,511,627,776) TB (terabyte) 10
12
(1,000,000,000,000)
Table 8 Decimal (radix) point character by locale
Language Character Examples
English, Chinese, Japanese, Korean Period (.) 146.81 GB
3.0 Gb/s
Dutch, French, German, Italian, Spanish Comma (,) 146,81 GB
3,0 Gb/s
