NDA-24300 CHAPTER 2
Page 17
Issue 1
SYSTEM MAINTENANCE OUTLINE
(a) Main Faults
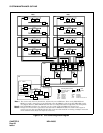
Faults that may occur in the system can be generally categorized into Processor System Fault, Speech
Path System Fault, Line/Trunk Fault, etc.
• Processor System Fault
The CPU alarm detecting circuit continuously monitors whether the CPU is working normally. If
a fault is detected, the CPU calls up the diagnostic program, which identifies the cause of the fault
and determines whether the fault is temporary or permanent. When the fault affects system
operations, Active/Standby status of the CPU is changed over (provided that the system has dual
configuration).
• Bus System Fault
The CPU transfers line/trunk card control information to the associated peripheral circuits via IO
Bus. When a parity error is detected in the transfer data or when the required information cannot
be transferred from a circuit card, the CPU identifies the cause of the fault, changes over the CPU
so that system operation is not affected, and executes restart processing.
• Speech Path Fault
The CPU monitors the operating status of the TSW card, the occurrence of errors in writing data
to the switch memory, and the basic clocks supplied to the speech path. Upon detecting a fault, the
CPU identifies the cause of the fault, determines whether the fault is temporary or permanent, and
executes required processing such as changeover of the TSW card.
•Others
The alarm detecting circuit on the EMA card continuously monitors the occurrence of faults in the
PWR supply cards, such as abnormal temperatures within the equipment frame, and lights the
alarm lamp on the TOPU when a fault is detected.
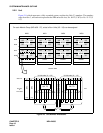
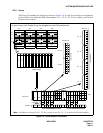
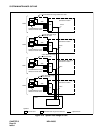
(b) Lamp Indications on the TOPU
When a fault occurs, the corresponding lamp on the TOPU indicates the location of the fault. For the
meaning of each lamp indication, refer to Chapter 6.