CHAPTER 2 NDA-24300
Page 30
Issue 1
SYSTEM MAINTENANCE OUTLINE
• The following is an example where the fault was recovered after the replacement of circuit cards:
(8) When a fault recovery is completed, use the RALM command to clear all the alarm indications and
registered system messages. If required, restore temporary cross connections and transient data for testing
to the original ones.
3.2 How to Follow Diagnostic Procedure/Fault Repair Procedure
(a) Diagnostic Work
A fault diagnostic procedure by system message is explained in the “TREE” format on an individual
system message basis.
• Proceed with judgment as to whether the fault status coincides with the indicated status, following
the sequence beginning from START.
• How to proceed with the diagnosis work is explained in Figure 2-24.
STEP 1 Determine whether the fault coincides with the fault status (1) in Figure 2-24.
STEP 2 If the fault status does coincide, the fault is indicated by (2). Repair the fault by referring to the
relevant section in Chapter 5. Otherwise, proceed to (3).
STEP 3 Perform the work indicated by (3). The result of the work (3) is broken down as indicated by
(4).
STEP 4 Determine whether the result of work (3) coincides with the status indicated by (5). If so, the
fault(s) is/are indicated either by (6) or by (7). If not, proceed to the next Step.
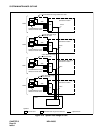
Set the 1st circuit card back into its mounting slot
If the fault recurs: Replace the circuit card.
Set the 2nd circuit card back into its mounting slot
If the fault recurs: Replace the circuit card.
Set the 3rd circuit card back into its mounting slot
If the fault recurs: Replace the circuit card.
If a circuit card is found to be faulty, send the faulty circuit card for repair.
The fault may be a temporary one, or due to poor contact of the circuit card. Observe the
situation for a while.
START
END