II - 3
Chapter 2 CPU Basics
Overview
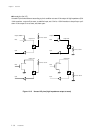
Figure 2-1-1 Block Diagram and Function
2-1-1 Block Diagram
A1
A0
D1
D0
D3
D2
T1
T2
Clock
generator
Source oscillation
Instruction execution
controller
Instruction decoder
Instruction
queue
Operand address
Program address
Program
counter
Incrementer
ALU
Address registers
Data registers
ABUS
BBUS
Interrupt bus
RAM busROM bus
Internal RAM
Internal ROM
Peripheral expansion bus
Internal peripheral
functions
SP
PSW
Processor status word
Stack pointer
Bus controller
Interrupt
controller
Clock generator
Uses a clock oscillator circuit driven by an external crystal or ceramic resonator to supply clock signals
to CPU blocks.
Program counter
Generates addresses for the instructions to be inserted into the instruction queue. Normally
incremented by sequencer indication, but may be set to branch destination address or ALU operation
result when branch instructions or interrupts occur.
Instruction queue Stores up to 2 bytes of pre-fetched instructions.
Instruction decoder
Decodes the instruction queue, sequentially generates the control signals needed for instruction
execution, and executes the instruction by controlling the blocks within the chip.
Instruction execution
controller
Controls CPU block operations in response to the result decoded by the instruction decoder and
interrupt requests.
ALU
Executes arithmetic operations, logic operations, shift operations, and calculates operand addresses
for register relative indirect addressing mode.
Internal ROM, RAM Assigned to the execution program, data and stack region.
Address register
Stores the addresses specifying memory for data transfer. Stores the base address for register relative
indirect addressing mode.
Data register Holds data for operations. Two 8-bit registers can be connected to form a 16-bit register.
Interrupt controller Detects interrupt requests from peripheral functions and requests CPU shift to interrupt processing.
Bus controller
Controls connection of CPU internal bus and CPU external bus. Includes bus usage arbitration
function.
Internal peripheral
functions
Includes peripheral functions (timer, serial interface, A/D converter, D/A converter, etc.) Peripheral
functions vary with model.