Chapter 2 CPU Basics
II - 24
Standby Functions
Transition to HALT modes
The system transfers from NORMAL mode to HALT0 mode, and from SLOW mode to HALT1 mode.
The CPU stops operating, but the oscillators remain operational. There are two ways to leave a HALT
mode: a reset or an interrupt. A reset produces a normal reset; an interrupt, an immediate return to the
CPU state prior to the transition to the HALT mode. The watchdog timer, if enabled, resumes counting.
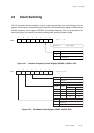
Program 4
MOV x'4', D0 ; Set HALT mode.
MOV D0, (CPUM)
NOP ; After written in CPUM, some NOP
NOP ; instructions (three or less) are
NOP ; executed.
Transition to STOP mode
The system transfers from NORMAL mode to STOP0 mode, and from SLOW mode to STOP1 mode. In
both cases, oscillation and the CPU are both halted. There are two ways to leave a STOP mode: a reset
or an interrupt.
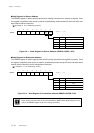
Program 5
MOV x'8', D0 ; Set STOP mode
MOV D0, (CPUM)
NOP ; After written in CPUM, some NOP
NOP ; instructions (three or less) are
NOP ; executed.
Right after the instruction of the transition to HALT, STOP mode, NOP instruction should be
inserted 3 times.