Chapter 6 8-bit Timers
VI - 16
8-bit Timer Count
02 03
M
NM
00 01 02 N-1
N
00 01
Count
clock
TMnEN
flag
Compare
register
Binary
counter
Interrupt
request flag
(A) (B)
(C)
(D)
(E)
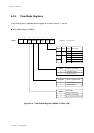
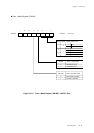
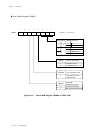
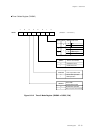
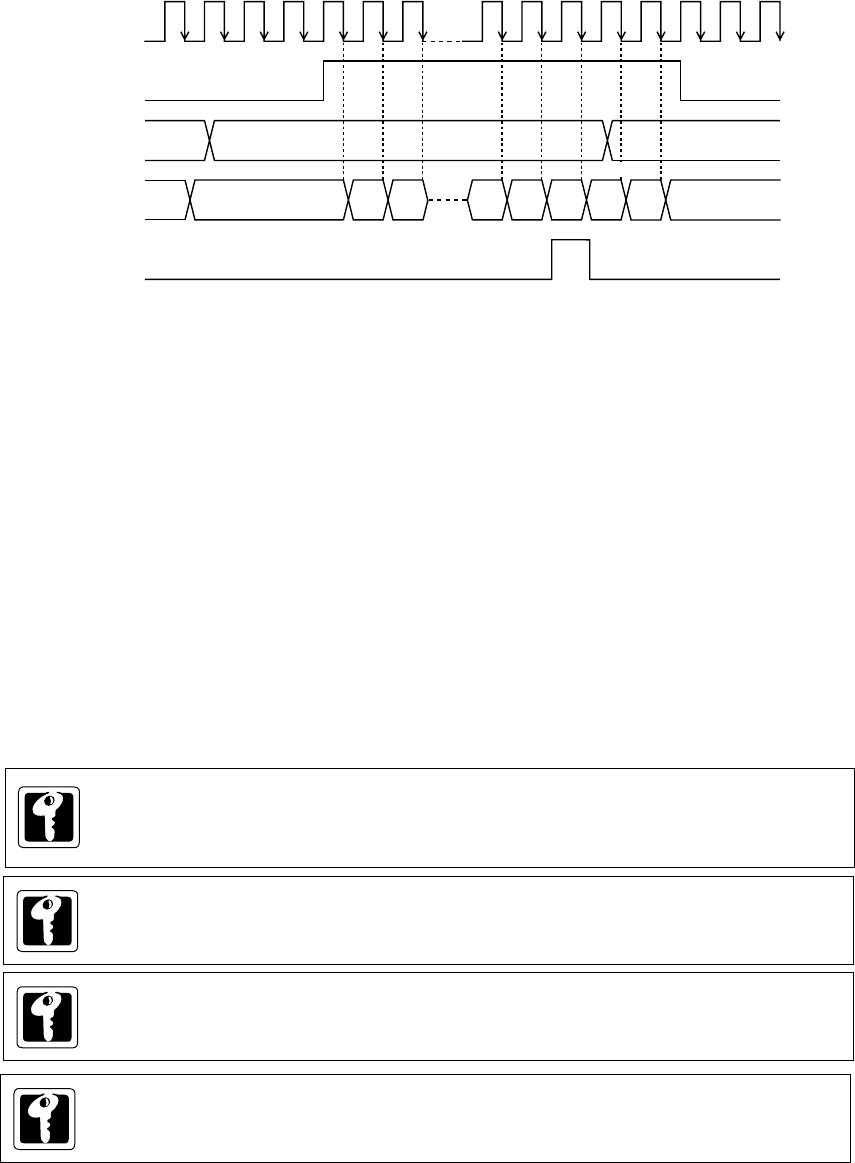
Count Timing of Timer Operation (Timers 0, 1, 4 and 5)
Binary counter counts up with selected clock source as a count clock.
The basic operation of the whole function of 8-bit timer is as follows ;
Figure 6-3-1 Count Timing of Timer Operation (Timers 0, 1, 4 and 5)
If the compare register is set the smaller than the binary counter during the count operation,
the binary counter counts up to the overflow, at first.
When the binary counter reaches the value in the compare register, the interrupt request flag
is set and the binary counter is cleared, at the next count clock. So set the compare register as:
Compare register setting = (count till the interrupt request - 1)
If the interrupt is enabled, the timer interrupt request flag should be cleared before timer
operation is started.
(A) If the value is written to the compare register during the TMnEN flag is "0", the binary counter
is cleared to x'00', at the writing cycle.
(B) If the TMnEN flag is "1", the binary counter is started to count.
The counter starts to count up at the falling edge of the count clock.
(C) If the binary counter reaches the value of the compare register, the interrupt request flag is
set at the next count clock, then the binary counter is cleared to x'00' and the counting is
restarted.
(D) Even if the compare register is rewritten during the TMnEN flag is "1", the binary counter is
not changed.
(E) If the TMnEN flag is "0", the binary counter is stopped.
The timer n interrupt request generation (at TMnOC = x'00') has the same waveform at
TMnOC = x'01'.