About This Manual 1
Organization
In this LSI manual, this LSI functions are presented in the following order : overview, basic CPU functions, interrupt
functions, port functions, timer functions, serial functions, and other peripheral hardware functions.
Each section contains overview of function, block diagram, control register, operation, and setting example.
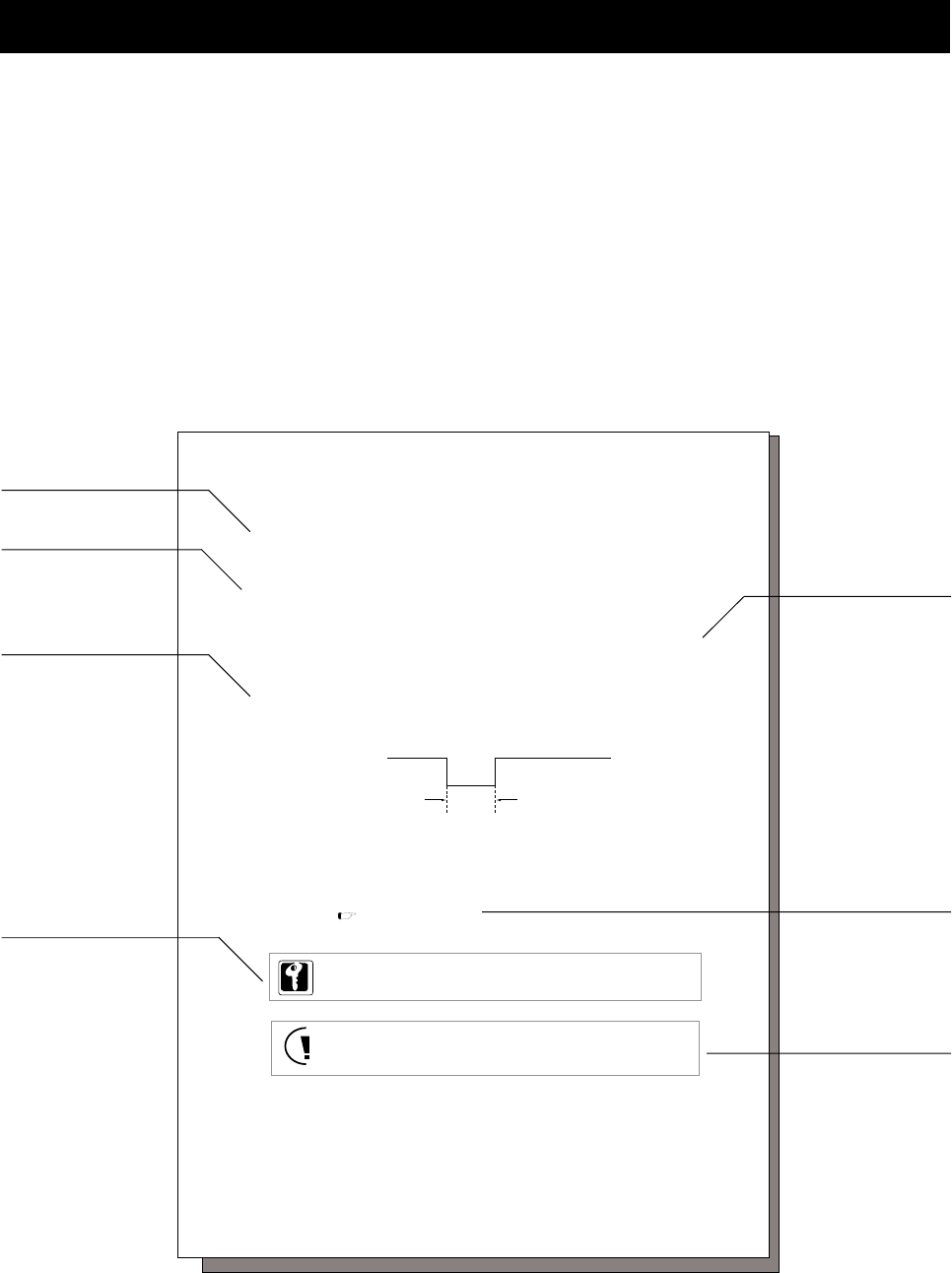
About This Manual
Manual Configuration
Each section of this manual consists of a title, summary, main text, key information, precautions and warnings, and
references.
The layout and definition of each section are shown below.
Sub-subtitle
The smallest block
in this manual.
Subtitle
Key information
Important information
from the text.
Main text
Precautions and
warnings
Precautions are listed
in case.
Be sure to read these
of lost functionality or
damage.
Summary
Introduction to the
section.
Chapter 2 Basic CPU
II - 44
Reset
2-8 Reset
2-8-1 Reset operation
The CPU contents are reset and registers are initialized when the NRST pin (P.27) is pulled to low.
Initiating a Reset
There are two methods to initiate a reset.
(1) Drive the NRST pin low for at least four clock cycles.
NRST pin should be holded "low" for more than 4 clock cycles (200 nS at a 20 MHz).
Figure 2-8-1 Minimum Reset Pulse Width
(2) Setting the P2OUT7 flag of the P2OUT register to "0" outputs low level at P27 (NRST) pin. And
transfering to reset by program (software reset) can be executed. If the internal LSI is reset and
register is initiated, the P2OUT7 flag becomes "1" and reset is released.
NRST pin
4 clock cycles
(200 nS at a 20 MHz)
[ Chapter 4. 4-4-2 Registers ]
On this LSI, the starting mode is NORMAL mode that high oscillation is the base clock.
When the power voltage low circuit is connected to NRST pin, circuit that gives pulse for
enough low level time at sudeen unconnected. And reset can be generated even if its pulse
is low level as the oscillation clock is under 4 clocks, take notice of noise.
References
References for the
main text.


















