III - 5
Chapter 3 Interrupts
Overview
3-1-3 Operation
■Interrupt Processing Sequence
For interrupts other than reset, the interrupt processing sequence consists of interrupt request, interrupt
acceptance, and hardware processing. The program counter (PC) and processor status word (PSW)
and handy addressing data (HA) are saved onto the stack, and execution branches to the address
specified by the corresponding interrupt vector.
An interrupt handler ends by restoring the contents of any registers used during processing and then
executing the return from interrupt (RTI) instruction to return to the point at which execution was inter-
rupted.
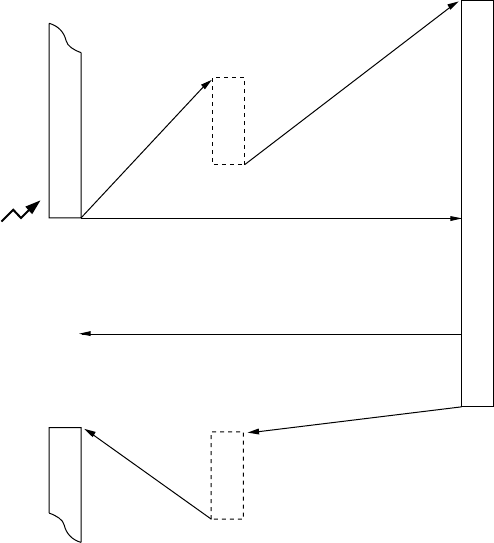
Figure 3-1-2 Interrupt Processing Sequence (maskable interrupts)
Interrupt service routine
Interrupt
request (xxxIR)
flag cleared
at head
Hardware processing
Save up
PC, PSW, etc.
Restore PSW, PC up, etc.
Interrupt
Main program
Restart
Max. 12 machine cycles
11 machine cycles
RTI