Nokia Network Voyager for IPSO 4.0 Reference Guide 415
Note
Make sure that IPSRD is not swapping memory. Look at the memory sizes occupied by
user-level daemons like Check Point, ifm, xpand, etc.
To find out how much memory IPSRD occupies, run the following command:
ps -auxww | grep ipsrd
The fourth column labeled, %MEM, displays the percentage of memory that IPSRD occupies.
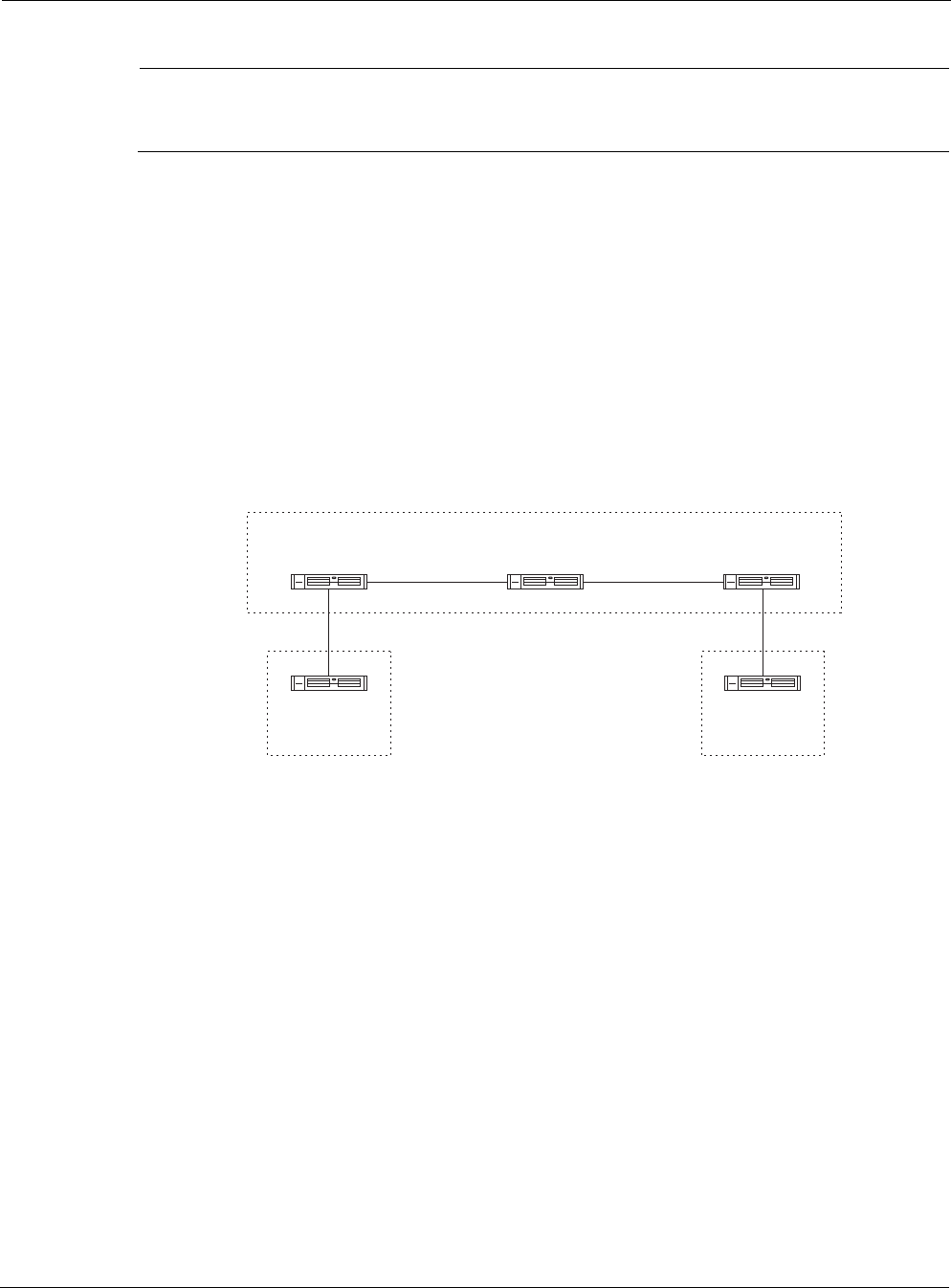
BGP Neighbors Example
BGP has two types: internal and external. Routers in the same autonomous system that exchange
BGP updates run internal BGP; routers in different autonomous systems that exchange BGP
updates run external BGP.
In the diagram below, AS100 is running IBGP, and AS200 and AS300 are running external BGP.
To configure IBGP on Nokia Platform A
1. Configure the interface as in “Ethernet Interfaces” on page 34.
2. Configure an internal routing protocol such as OSPF or configure a static route to connect
the platforms within AS100 to each other.
For more information see “Configuring OSPF” on page 356 or “To configure a default or
static route” on page 395.
3. Click BGP under Configuration > Routing Configuration in the tree view.
4. Enter a router ID in the Router ID text box.
The default router ID is the address of the first interface. An address on a loopback interface
that is not the loopback address (127.0.0.1) is preferred.
5. Enter 100 in the AS number text box.
6. Enter 100 in the Peer autonomous system number text box.
7. Click Internal in the Peer group type drop-down list; then click Apply.
Nokia
Platform A
Nokia
Platform D
Nokia
Platform B
AS100
IBGP
EBGP
00331
10.50.10
129.10.21
IBGP
170.20.1
.1
.1
.2
.2
.2
Nokia
Platform C
.1
.1
AS200
Nokia
Platform E
EBGP
172.17.10
.2
AS300